At
SMAU of Padua held in April 2013
C.R.A.M. (
Anti-Malware Research Center) presented a detailed
repor [
report available only in Italian] on two new infections that were hitting the Italian users (and not only) named
FakeGDF and
ZeroAccess.
Now, a new infection taking advantage of similar mining techniques used by
ZeroAccess is spreading in Italy.
In addition to
pc click-fraud and the download of additional infections like:
fraudtool,
Trojan clicker and ransomware (
FakeGDF),
ZeroAccess shows a special peculiarity: relying on an army of compromised computers, it uses their computing power for an activity known as: Bitcoin mining.
Bitcoin is an electronic money created back in 2009 from an anonymous figure only known with the name of
Satoshi Nakamoto, this currency can’t be monopolized by any banks, instead, it is uniformly distributed through the network. Leveraging on the computing power of all infected computers,
ZeroAccess makes them perform complex computational tasks; For each calculation performed successfully it receives a reward in Bitcoin that can be converted at a later time, in a different currency (USD, Euro, etc.).
The
Trojan.Win32.Agent.EDM shares with
ZeroAccess the structure of exploitation of compromised computers, unlike Bitcoin, the
Trojan.Win32.Agent.EDM ensures for itself a constant earning using Litecoin mining.
From a technical point of view, Litecoin currency is identical to Bitcoin, the creation and the transfer of this electronic money is based on an open source cryptographic protocol known as
scrypt.
The
Trojan.Win32.Agent.EDM makes the most from the Litecoin currency since the mining can be executed in an efficient way on common end user computers. The algorithm used by Litecoin, as stated before, is based on
scrypt , this approach promotes the use of miner on normal computer and between the most common GPU present today on the market, all this without slowing down the computer performance.
The activity performed by the
Trojan.Win32.Agent.EDM can be split in different parts:
|
Phase #1
On the victim’s computer, the file initsrv.exe is put in auto execution, adding the executable file to the following path::
C:\Documents and settings\Users \Start Menu\Programs\Startup\initsrv.exe
In this way, the malicious file can be run each time the computer is started.
Phase #2
initsrv.exe is started from the dropper that has put it on the computer
Fase 2.1:
Immediately after execution, initsrv.exe, starts verifying in the following path: %SystemRoot%/system32/ the presence of three different files:
- libcurl-4.dll
- pthreadGC2.dll
- minerd.exe
If not detected, initsrv.exe downloads the page
http://pastebin.com/raw.php?i=sw[XXXXXXXX]
from which are extracted the necessary URLs to download each file searched at the beginning of the infection process.
|
 |
Pastebin, known web application for sharing fragments of text, is used by the
Trojan.Win32.Agent.EDM to extract, through array, all the strings inside the downloaded page.

As shown in the image above, each line is made up by
[file name]:: URL
If
[name file].exe / .dll is not found inside the PATH
%SystemRoot %/system32/, the
Trojan.Win32.Agent.EDM starts the download of the required file through the associated URL.
If all three files searched are found, the variable
check_passed, used for track the status of the search, is equal to
True, this allows the program to move on to the next part of the malicious code. Below the flowchart of the first part of the malicious code
 |
| infection flow |
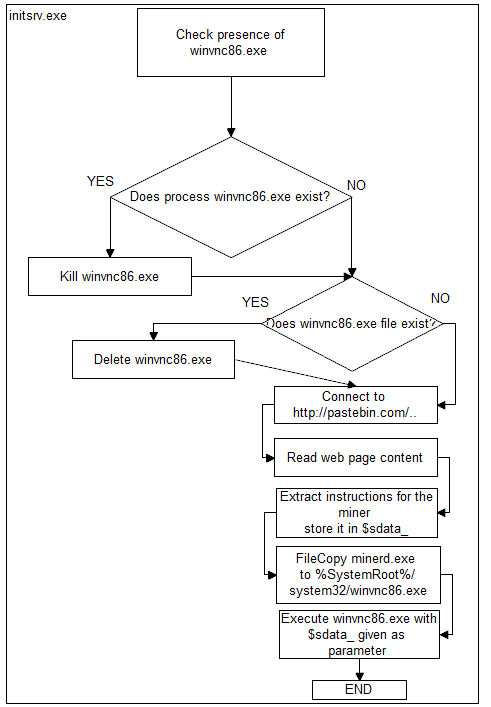
Phase 2.2:
If phase 2.1 is completed successfully, the malware enters in phase 2.2.
initsrv.exe starts a sequence of checks in order to verify the presence of the file / process
winvnc86.exe
- Checks the presence in memory of the process winvnc86.exe, if found, it is killed.;
- Checks the presence of the file winvnc86.exe in %SystemRoot %/system32/, if found, it is erased.
After the two audit,
inisrv.exe downloads the page
http://pastebin.com/raw.php?i=sw[XXXXXXXX] (the link is different from the one shown before), from the required web page it extracts a string of instructions, memorizing them in the
sdata_ variable.
String value of commands, downloaded by inisrv.exe
 |
Legend commands downloaded:
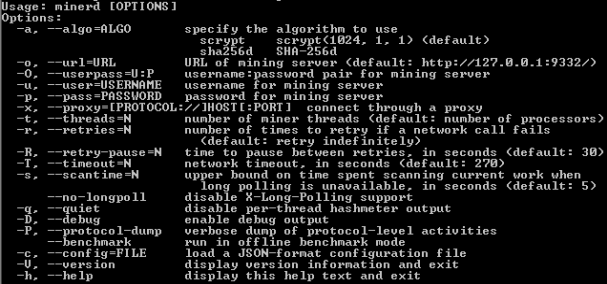 |
Relying on a function
FileCopy, initsrv.exe takes the minerd.exe file from
%SystemRoot%/system32/ and creates a copy of the same in
%SystemRoot %/system32/ naming it
winvnc86.exe
The last set of instructions executes
winvnc86.exe , passing as a parameter the variable
sdata_ that stores the instructions for the miner.
Below the flowchart describing the execution of the second part of the infection:
 |
| infection flow |
When the
Trojan.Win32.Agent.EDM (
initsrv.exe) terminates correctly its execution, has already been able to start the miner ( playing the user), making he / she believe that the process is a trusted application:
winvnc86.exe
Despite the minerd.exe file, downloaded during the infection, is a legitimate one and the source code can be downloaded from sourceforge.net, this application is detected by
Vir.IT eXplorer as
Trojan.Win32.Agent.BHTO; This because analyzing different situation where winvnc86.exe (aka minderd.exe) was implied the presence of
Trojan.Win32.Agent.EDM was every time confirmed.
At every PC restart, the
Trojan.Win32.Agent2.BHTO is executed and the infection cycle takes place again:
- initsrv.exe checks the presence of the files required to start the Litecoin mining;
- If files doesn’t exists, download them;
- Kill the process winvnc86.exe / erase the file winvnc86.exe;
- Download parameters for the miner;
- Copy and rename the file minerd.exe in winvnc86.exe;
- Start winvnc86.exe with the parameters stored in the variable sdata_ in order to contact the mining pool server.
Mining pool server are accessible by anyone, create a new user is easy and straightforward, in the first stage, the criminal creates two couples of user name and password.
The first pair of user name and password are used to access the mining pool server and view the status of earnings, the second pair is given instead as a parameter to all miners distributed during infection.
The system of double credentials was introduced for safety reasons, as each running miner will send user name and password credential in clear and obviously can be intercepted easily.
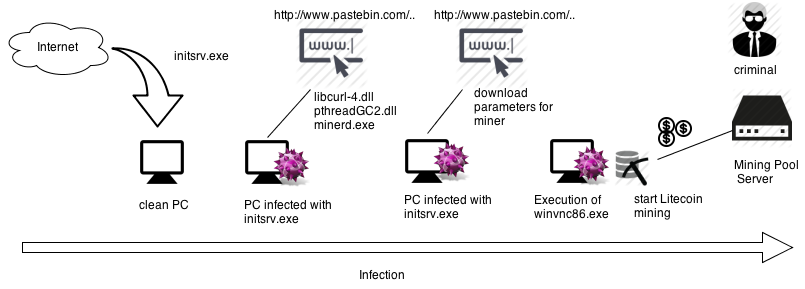
Below, the complete infection flow when a user comes in contact with
inisrv.exe
---------------------------------
CRAM (Centro Ricerche Anti-Malware) di TG Soft







