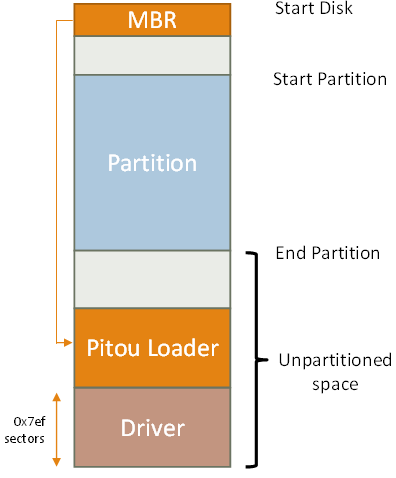
Pitou uses the "standard" technique of infection of the MBR. It overwrites the last 1 MB with the loader of Pitou and the Driver in the unpartitioned space.
In the first 17 sectors of the last 1 MB there is the code of loader of Pitou and in the following sectors there is the Driver (kernel payload) in encrypted form.
| Here we can see the dump of MBR infected: |
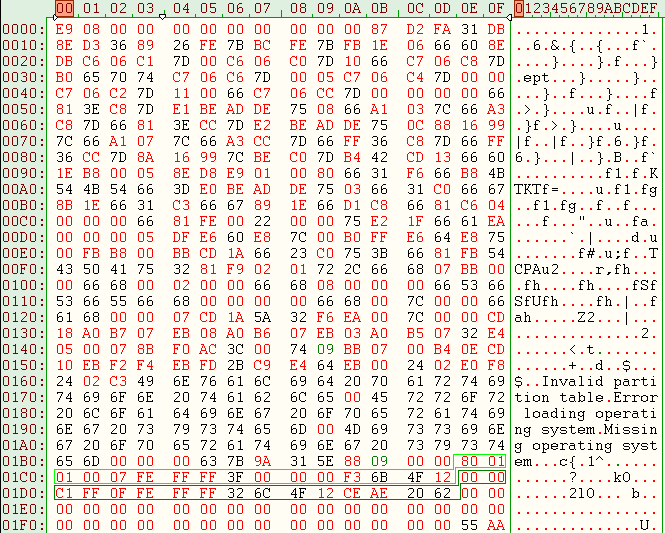 |
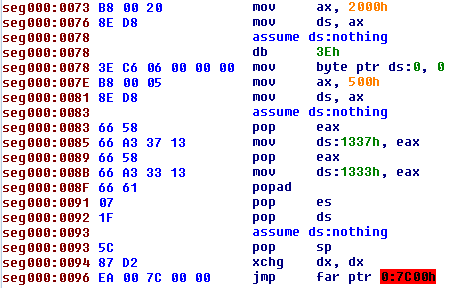
The code of MBR infected by Pitou reads the 17 sectors at end of disk (in the unpartitioned space) in memory at address 500:0 as we can see here:
The 17 sectors are encrypted, so Pitou decrypts it with this easy algorithm (xor and ror):
The next step is hook the int 13h at address 500:9Bh:
After that Pitou has hooked the int 13h, it decrypts the original MBR at address 0:7C00h and executes it.
Switch from Real Mode to Protect Mode
Now that Pitou has passed the control at original MBR, Pitou is hooked only at int 13h. Here we can see the routine of int 13h of Pitou:
The routine Pitou detects each request of read of sectors, function ah=42h (Extended Read Sectors) and ah=02h (Read Sectors), this permits at Pitou to know when the process of boot will read the file C:\NTLDR or C:\BOOTMGR.
In this step Pitou must hook C:\NTLDR or C:\BOOTMGR for "survive" when there is the switch from real mode into protect mode:
Pitou patches "ntldr" with:
- xxxxxxxx call gate selector 8:600h
- 00000600 jmp 0x5183
The first patch is "call gate selector 8:600h", so the "ntldr" will go at address 0x00000600. At address 0x00000600 Pitou has patched this area of memory with "0xe9 0x7e 0x4b 0x0 0x0" so jump (jmp) at address 0x00005183 (0x600 + 0x4b7e + 0x5 = 0x5183)
The address 0x00005183 in protect mode is equal in real mode at address 500:0183 where Pitou is saved in this moment.
Now Pitou is working in protect mode, but the area of memory where Pitou is saved can be overwritten by Windows or the memory can be paged.
So Pitou needs to allocate "safe" memory, it will allocate 2 pages and it will copy the loader at 32 bit in the new area of memory.
Now Pitou parses the NTLDR to hook the call at function KiSystemStartup. The hook is made before the NTLDR calls KiSystemStartup, because at thata moment the NLDR has loaded the "NTOSKRNL.EXE" but not executed. The hook permits to Pitou to know the base of address of module "NTOSKRNL.EXE", then Pitou will parse the module "NTOSKRNL.EXE" to insert a new hook.
The last hook in "NTOSKRNL.EXE" permits to Pitou to know that the kernel of Windows (NTOSKRNL.EXE) is running properly.
Now Pitou can use the API exported by NTOSKRNL.EXE:
Pitou creates a new system thread calling the function PsCreateSystemthread exported by NTOSKRNL.EXE. The thread will load the driver bypassing the
Microsoft Kernel-Mode Code Signing policy.
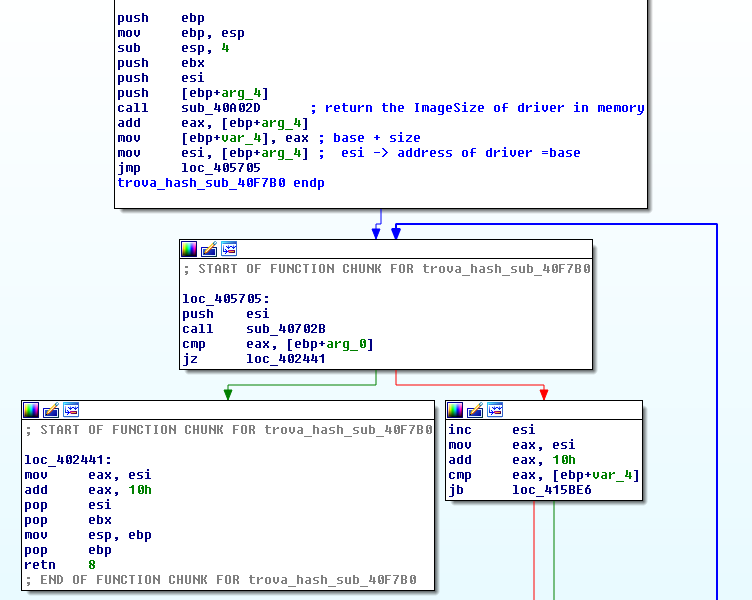
In this phase Pitou will do:
- Allocate 0xfde00 bytes in memory ("physical memory" )
- Read and decrypt the last 0x7ef sectors of disk in the "physical memory"
- Allocate a buffer with size equal at ImageSize of driver for the "virtual memory"
- "Load" the driver from "physical memory" to "virtual memory"
- Create the structure "DriverObject" to pass at Entrypoint of driver
|
 |
Here we can see as Pitou execute the driver:
Back on top
Pitou on Windows 10 64 bit
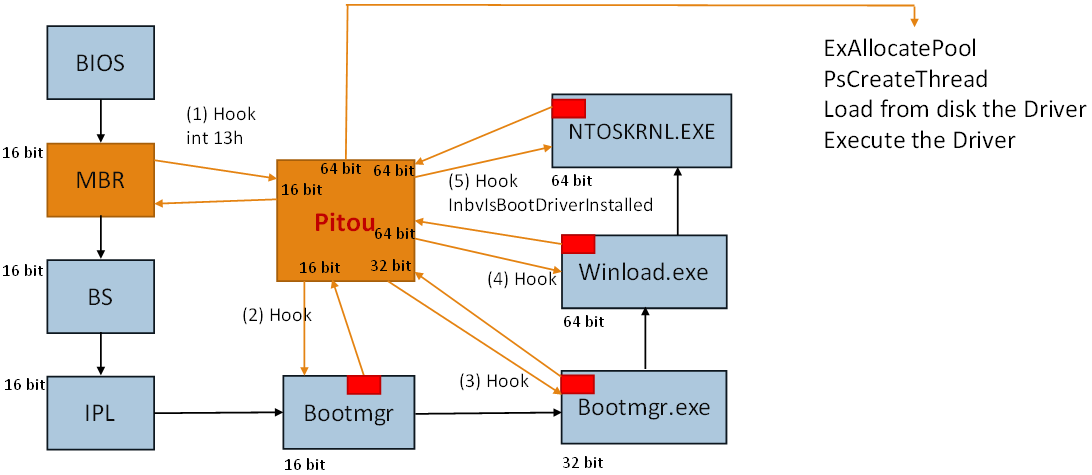
The loader of Pitou on Windows 10 64 bit uses 3 different codes:
- 16 bit (from BIOS to Bootmgr)
- 32 bit (from Bootmgr to Bootmgr.exe)
- 64 bit (from Winload.exe to NTOSKRNL.EXE)
In the scheme the point 1 indicates the hook at int 13h by Pitou to know when the "Bootmgr" is read. The second hook is made inside the "Bootmgr" to swtich from real mode into protect mode. In this phase the "Bootmgr" will extract from it a file PE dubbed "Bootmgr.exe". The file "Bootmgr.exe" works in 32 bit and is executed by Bootmgr. At this point Pitou (32 bit) will hook the "Bootmgr.exe" to know when it will load the file "Winload.exe" (64 bit). This hook is need to survive at switch from 32 bit to 64 bit. When this hook is called, Pitou (64 bit) will parse the file "Winload.exe" to hook when "Winload.exe" will load and execute the "NTOSKRNL.EXE". When the hook inside "Winload.exe" is called, then Pitou will parse "NTOSKRNL.EXE" to hook the function "InbvIsBootDriverInstalled".
The last hook in the function "InbvIsBootDriverInstalled" is need to know when "NTOSKRNL.EXE" is loaded and ready.
As in the previous case, Pitou will load the driver 64 bit bypassing the
Microsoft Kernel-Mode Code Signing policy.
Back on top
Pitou Driver 32bit
We have analyzed the driver 32 bit of Pitou, the 64 bit version is similar.
The driver extracted from the end of disk has the following characteristics:
Size: 437.248 byte
MD5: EA286ABDE0CBBF414B078400B1295D1C
Compilation Time Date Stamp: 10 July 2017 15:59:35
No submission on VT
Fully obfuscated: difficult to analyze in static way
Anti-VM
Stealth
SpamBot (works completely in kernel mode)
Obfuscation
The driver is obfuscated as we can see:
It contains a lot of random strings as "Again, one can talk, for to kill" to evade the AVs. |
 |
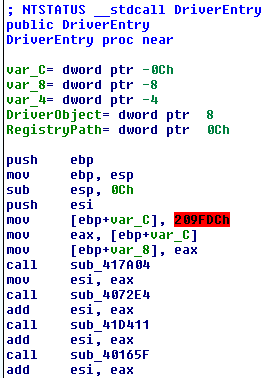
We can see some levels of obfuscation. The first level is at "DriverEntry":
The DriverEntry sets a local variable [ebp+var_C] with value 0x209fdc, after it calls a lot of subroutines that modifies this value each time until to arrive to call the subroutine "call [ebp+var_C]" with the real "DriverEntry".
A second level of obfuscation is the use of hashes of blocks of 16 byte of code/data to calculate the addresses of objects, structures, strings, data and etc.
These hashes change everytime with the execution of drivers, so it is very difficult to take a snapshot for the analysis.
Here an example:
Anti-VM
Pitou checks if it is running under VM, Sandboxing or in emulated/virtualized environments:
- MS_VM_CERT, VMware -> VMWare
- Parallels -> Paralles Desktop for Mac
- SeaBIOS -> SeaBIOS emulator
- i440fx, 440BX -> QEMU emulator
- Bochs -> Bochs emulator
- QEMU0 -> QEMU emulator
- VRTUALMICROSFT -> Hyper-V
- Oracle, VirtualBox -> Oracle VM VirtualBox
- innotek -> Innotek VirtualBox (Oracle VM VirtualBox)
If it is running under VM or in emuIated/virtualized environments then it stops to work.
Stealth
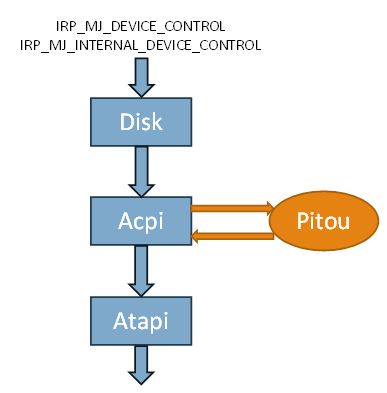
Pitou uses technique to be stealth, as other bootkits, it hooks the Miniport Device Object of disk to detect the request of read/write of sectors of disk:
- IRP_MJ_DEVICE_CONTROL
- IRP_MJ_INTERNAL_DEVICE_CONTROL
\Driver\ACPI -> MajorFunction[IRP_MJ_DEVICE_CONTROL] = 81aefe43 Hook in ???
81aefe43 55 push ebp
81aefe44 8bec mov ebp,esp
81aefe46 51 push ecx
81aefe47 53 push ebx
81aefe48 8b5d08 mov ebx,[ebp+0x8]
81aefe4b 33c0 xor eax,eax
\Driver\ACPI -> MajorFunction[IRP_MJ_INTERNAL_DEVICE_CONTROL] = 81ae9a5f Hook in ???
81ae9a5f 55 push ebp
81ae9a60 8bec mov ebp,esp
81ae9a62 83e4f8 and esp,0xf8
81ae9a65 83ec24 sub esp,0x24
81ae9a68 833d68b9b48100 cmp dword ptr [81b4b968],0x0
81ae9a6f 8b4d0c mov ecx,[ebp+0xc]
|
When an application in "user mode" send a request to read the MBR, this is intercepted by Pitou in kernel mode, that instead will read the original MBR at end of disk hiding the infection.
Above we can see the hook in the miniport of device "ACPI" on: IRP_MJ_DEVICE_CONTROL and IRP_MJ_INTERNAL_DEVICE_CONTROL |
 |
Server C/C
Pitou connects at server C/C with IP 195.154.237.14 Port 7384 TCP, and is hosted in Paris.
In encrypted form it receives commands to send spam:
- email addresses
- body
- smtps
If Pitou cannot connect at server C/C then it generates 4 domains (DGA), examples:
- unpeoavax.mobi
- ilsuiapay.us
- ivbaibja.net
- asfoeacak.info
SpamBot
Pitou sends spam from the pc of victim, this operation is made totally in kernel mode.
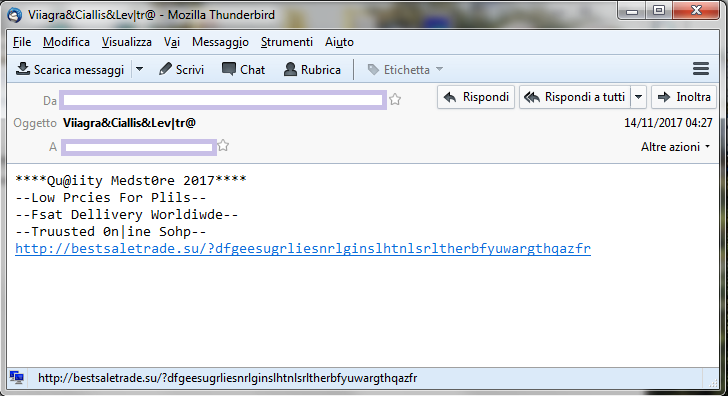
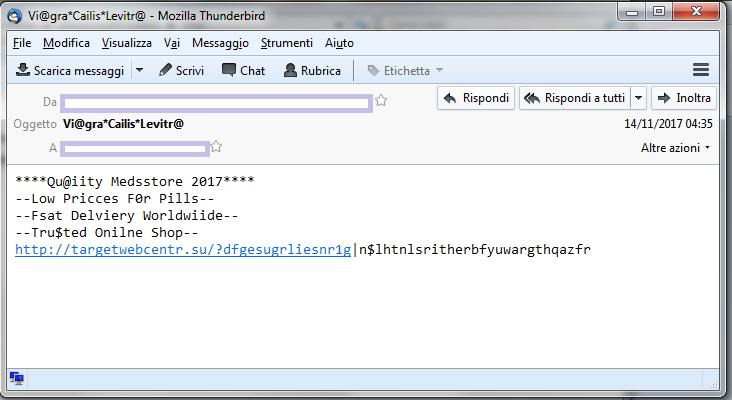
Here some example of spam sent by Pitou:
As you can see Pitou sends spam of Viagra and Cialis.